Background
Generally speaking, the game server will cache some player status data locally. During automatic elastic scaling, the Carrier controller cannot create or delete GameServer at will. The Statefulset, Deployment and other workloads provided by K8s lack confirmation with the application when shrinking, changing and deleting Pods.
The GameServer workload provides a simple SDK. The game backend server can notify the Carrier controller of some current service status information, which is used to select the appropriate copy to delete when the Carrier controller elastically expands or releases changes.
The relationship between GameServer and Carrier SDK
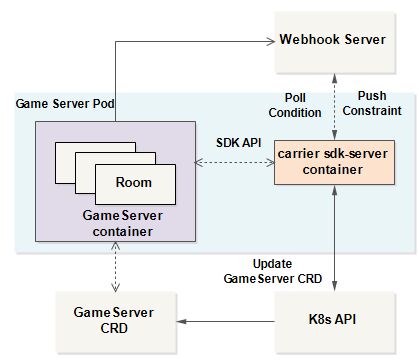
SDK-Serveracts as a sidecar container (automatically injected by theCarriercontroller) and runs on the same K8s pod as theGameServercontainer.GameServercan accessSDK-Serverthrough SDK API. If the application does not want to call the SDK API, you can configure the corresponding Webhook, and theSDK-Serverwill call the Webhook.SDK-Serverconnects to K8s API and updatesGameServerCRD.
User-defined conditions
GameServer can set custom conditions through SDK API or Webhook.
ReadinessGates
kind: GameServer
...
spec:
readinessGates:
- network.ocgi.dev/lb-ready
status:
conditions:
- type: "network.ocgi.dev/lb-ready"
status: "True"
lastProbeTime: null
lastTransitionTime: 2018-01-01T00:00:00Z
When the Squad is updating or scaling, it needs to ensure that all ReadinessGates condition are True before the Carrier controller considers the new replica status to be Ready.
DeletableGates
kind: GameServer
...
spec:
deletableGates:
- carrier.ocgi.dev/has-no-player
status:
conditions:
- type: "carrier.ocgi.dev/has-no-player"
status: "True"
lastProbeTime: null
lastTransitionTime: 2018-01-01T00:00:00Z
When Squad is updating or scaling down, you need to ensure that the DeleteableGates condition is True before you can delete the corresponding replica.
GameServer acccess the SDK Server
After the SDK-Server is started, it will listen to a gRPC and an HTTP port, and the Carrier controller will write the port information as an environment variable to the GameServer container:
# kubectl exec -it squad-example-54b764fd57-2bkhx -c server /bin/bash
[root@squad-example-54b764fd57-2bkhx /]# env | grep SDK
CARRIER_SDK_GRPC_PORT=9020
CARRIER_SDK_HTTP_PORT=9021
- CARRIER_SDK_GRPC_PORT: gRPC service port, the default is 9020
- CARRIER_SDK_HTTP_PORT: http service port, the default is 9021
SDK API
Refer to SDK gRPC API and SDK HTTP API.
simple-tcp is an example of using go sdk.
sdk-examples-cpp is an example of using c++ sdk.
User-defined Webhook
If the application does not want to call the SDK API, you can configure the corresponding Webhook, and the SDK-Server will call the Webhook.
- First, we define a Webhook service. E.g:
apiVersion: carrier.ocgi.dev/v1alpha1
kind: WebhookConfiguration
metadata:
name: ds-webhook
namespace: default
webhooks:
- clientConfig:
url: http://ds.carrier.dev/server-ready
name: server-ready
type: ReadinessWebhook
Details abount Webhook, please refer to WebhookConfiguration.
// WebhookConfiguration is the data structure for a WebhookConfiguration resource.
type WebhookConfiguration struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"`
Webhooks []Configurations `json:"webhooks"`
}
// +k8s:deepcopy-gen:interfaces=k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime.Object
// WebhookConfigurationList is a list of WebhookConfiguration resources
type WebhookConfigurationList struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
metav1.ListMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"`
Items []WebhookConfiguration `json:"items"`
}
type Configurations struct {
ClientConfig v1.WebhookClientConfig `json:"clientConfig"`
Name *string `json:"name,omitempty"`
Type *string `json:"type,omitempty"`
TimeoutSeconds *int32 `json:"timeoutSeconds,omitempty"`
PeriodSeconds *int32 `json:"periodSeconds,omitempty"`
}
Where Type can be
ReadinessWebhook
Corresponding to the value in the Name of the Configurations readinessGates
DeletableWebhook
Corresponding to the value in the Name of the configuration deletableGates
ConstraintWebhook
After the ConstraintWebhook is configured, the SDK server will automatically watch the Constraint of the Gameserver, and then call the user’s webhook
- Configure GameServer to access Webhook.
apiVersion: carrier.ocgi.dev/v1alpha1
kind: GameServer
metadata:
annotations:
carrier.ocgi.dev/webhook-config-name: ds-webhook # should be the webhook name
name: ds-server
namespace: default
spec:
readinessGates:
- server-ready # readiness gate name should be same as the readiness gate name in webhook
3.Webhook Server
Please refer to webhook example.
Webhook server API
// WebhookRequest defines the request to webhook endpoint
type WebhookRequest struct {
// UID is used for tracing the request and response.
UID types.UID `json:"uid"`
// Name is the name of the GameServer
Name string `json:"name"`
// Namespace is the workload namespace
Namespace string `json:"namespace"`
// Constraints describes the constraints of game server.
// This filed may be added or changed by controller or manually.
// If anyone of them is `NotInService` and Effective is `True`,
// We should react to the constraint.
Constraints []Constraint `json:"constraints,omitempty"`
}
// WebhookResponse defines the response of webhook server
type WebhookResponse struct {
// UID is used for tracing the request and response.
// It should be same as it in the request.
UID types.UID `json:"uid"`
// Set to false if should not allow
Allowed bool `json:"allowed"`
// Reason for this result.
Reason string `json:"reason,omitempty"`
}
// Constraint describes the constraint info of game server.
type Constraint struct {
// Type is the ConstraintType name, e.g. NotInService.
Type string `json:"type"`
// Effective describes whether the constraint is effective.
Effective *bool `json:"effective,omitempty"`
// Message explains why this constraint is added.
Message string `json:"message,omitempty"`
// TimeAdded describes when it is added.
TimeAdded *time.Time `json:"timeAdded,omitempty"`
}
// WebhookReview is passed to the webhook with a populated Request value,
// and then returned with a populated Response.
type WebhookReview struct {
Request *WebhookRequest `json:"request"`
Response *WebhookResponse `json:"response"`
}
The webhook server will receive the
WebhookReview, but only contains theRequest, and the webhook server returns theWebhookReview, but it needs to contain theResponse;For
ReadinessWebhookandDeleteableWebhook, the receivedRequestwill containGameServer Name,Namespace, and the webhook server’sResponseneeds to returnAllowed,Reason (optional);For
ConstraintWebhook, the receivedRequestwill includeGameServer Name,Namespace,Constraint. The webhook server’sResponsemay not return any valid information, and the sdk-server does not currently verify the return information.
Reference
For more information, please refer to the carrier-sdk.